The Stages of Sleep Explained: REM, Deep & Light – Understanding Sleep Cycles, Brain Activity, and Restorative Healing
🌙 Why Understanding Your Sleep Stages Matters
If you’ve ever woken up groggy after a “full” night of sleep, wondered why you dream more on some nights, or struggled with restlessness, you’ve likely felt the effects of poor sleep architecture — the structure of your sleep cycle.
Even if you spend eight hours in bed, the quality of those hours depends on how much time you spend in light sleep, deep sleep, and REM sleep. These stages work together like gears in an engine. When one is off balance, the whole system struggles.
This guide gives you the stages of sleep explained in simple, science-based language — perfect for anyone dealing with insomnia, overthinking, or nighttime anxiety. Understanding how sleep cycles work can help you improve rest, energy, mood, and long-term health.
🌙 The Stages of Sleep Explained: An Overview
Sleep is not a single state — it’s a repeating cycle of phases, each with its own purpose.
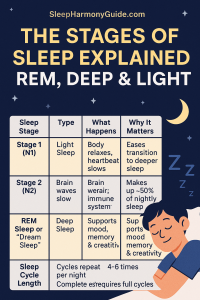
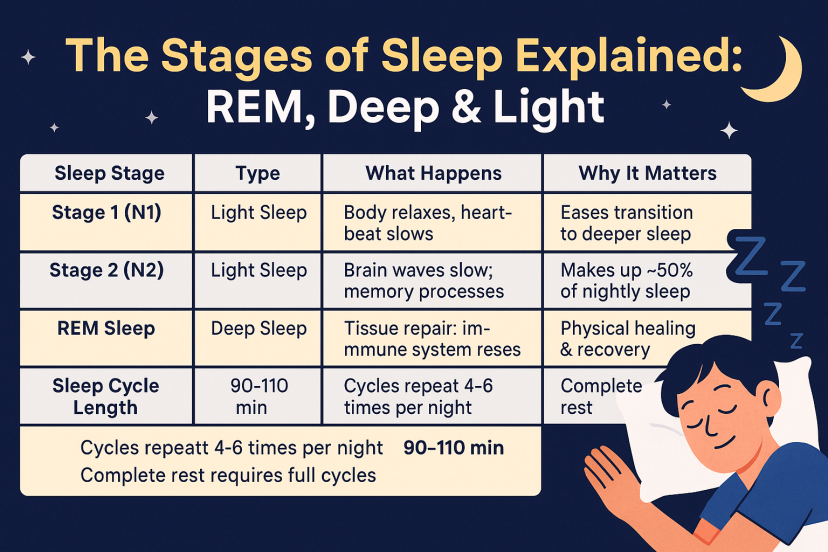
Sleep Stage | Type | What Happens | Why It Matters
———————————————————————————————–
Stage 1 (N1) | Light Sleep | Body relaxes, heartbeat slows | Eases transition to deeper sleep
Stage 2 (N2) | Light Sleep | Brain waves slow; memory processes | Makes up ~50% of nightly sleep
Stage 3 (N3) | Deep Sleep | Tissue repair; immune system resets | Physical healing & recovery
REM Sleep | Dream Sleep | Brain active; emotional processing | Mood, memory & creativity support
———————————————————————————————–
Sleep Cycle Length | 90–110 min | Cycles repeat 4–6 times per night | Complete rest requires full cycles
Knowing these stages helps you identify where your sleep may be breaking down — and how to fix it.
🌙 Light Sleep Stages Explained (N1 & N2)
What Light Sleep Does for Your Brain and Body
Light sleep is the entry point into deeper sleep stages. It makes up ~50–60% of your total nightly sleep.
Key functions include:
-
Stabilizing Heart Rate And Breathing
-
Beginning Memory Processing
-
Reducing Muscle Tension
-
Lowering Stress Hormones
-
Preparing Your Body For Deep Sleep
Signs You’re Not Getting Enough Light Sleep
-
Frequent Waking Up At Night
-
Difficulty Transitioning Into Deeper Stages
-
Feeling Restless Or Easily Startled
How To Improve Light Sleep
-
Maintain A Consistent Bedtime
-
Reduce Evening Screen Time
-
Use White Noise Machines Or Fans
-
Keep Room Temperature Cool (65–68°F)
🌙 Deep Sleep Explained (Slow-Wave Sleep / N3)
What Deep Sleep Is & Why It’s Essential
Deep sleep — also known as slow-wave sleep — is the most restorative sleep stage.
During this stage:
-
Tissue Repair Occurs
-
Growth Hormone Is Released
-
Immune System Strengthens
-
Muscle Recovery Begins
-
Body Detoxification Processes Activate
It’s especially important for adults who exercise, work physically demanding jobs, or deal with high stress.
How Much Deep Sleep Do You Need
Most adults need 1–2 hours per night, though athletes may need more.
Signs You’re Lacking Deep Sleep
-
Morning Grogginess
-
Low Immune Function
-
Muscle Soreness
-
Intense Sugar Cravings
-
Slow Reaction Times
How To Increase Deep Sleep
-
Avoid Late Caffeine
-
Try Magnesium Glycinate
-
Use Weighted Blankets
-
Limit Alcohol Before Bed
-
Exercise Regularly (But Not Too Late)
🌙 REM Sleep Explained (Rapid Eye Movement)
What REM Sleep Does for the Mind
This is the dream stage of sleep. It is essential for:
-
Emotional Processing
-
Stress Regulation
-
Learning & Memory Consolidation
-
Creativity & Problem Solving
During REM, your brain becomes almost as active as when you’re awake — but your body remains relaxed.
How Much REM Sleep You Need
Most adults need 90–120 minutes of REM sleep per night.
Signs You’re Not Getting Enough REM Sleep
-
Emotional Sensitivity
-
Difficulty Concentrating
-
Memory Issues
-
Increased Anxiety Or Irritability
How To Support Healthy REM Sleep
-
Stick To A Sleep Schedule
-
Avoid Alcohol Late At Night
-
Use Lavender Or Chamomile For Stress Relief
-
Create A Dark, Quiet Bedroom Environment
🌙 How Sleep Cycles Work
Every night, your body moves through 4–6 full sleep cycles, each lasting 90–110 minutes.
Each cycle includes:
-
Light Sleep → Deep Sleep → REM
Early cycles contain more deep sleep, while later cycles contain more REM sleep.
Breaking this cycle — with alarms, nighttime awakenings, late bedtimes, or screens — reduces the amount of restorative sleep you’re getting.
🌙 Why Your Sleep Cycles May Be Disrupted
Many U.S. adults struggle with interrupted sleep architecture due to:
-
Stress And Racing Thoughts
-
Irregular Bedtimes
-
Overuse Of Screens
-
Caffeine Or Sugar Late In The Day
-
Alcohol Near Bedtime
-
Chronic Pain
-
Undiagnosed Sleep Disorders
Disrupted cycles lead to poor sleep quality even when you’re in bed for 7–9 hours.
🌙 Lifestyle Strategies to Improve All Stages of Sleep
Strengthen Your Circadian Rhythm
-
Wake Up At The Same Time Daily
-
Get 10–20 Minutes Of Morning Sunlight
-
Avoid Sleeping In On Weekends
Build A Consistent Wind-Down Routine
-
Dim The Lights
-
Take A Warm Shower
-
Drink Herbal Tea (Chamomile, Lemon Balm)
-
Use Relaxing Music Or White Noise
-
Stretch Or Do Gentle Yoga
Use Sleep-Supporting Supplements
-
Melatonin (Low Dose For Timing)
-
Magnesium Glycinate For Relaxation
-
Lavender Aromatherapy For Calmness
Create A Sleep-Friendly Bedroom
-
Blackout Curtains For Darkness
-
Cooling Mattress Or Pillow
-
White Noise Machine Or Fan
-
Clutter-Free, Calm Environment
🩺 When To See A Doctor About Sleep Cycle Problems
Consult a sleep specialist if you experience:
-
Trouble Sleeping At Least 3 Nights Per Week
-
Loud Snoring, Gasping, Or Pauses In Breathing
-
Severe Insomnia Or Early Morning Awakening
-
Excessive Daytime Fatigue
-
Chronic Pain Interrupting Sleep
-
Nightmares Or Disturbing Dream Patterns
A sleep specialist may recommend:
-
CBT-I Therapy
-
A Sleep Study (Polysomnography)
-
Medication (If Appropriate)
❓ Frequently Asked Questions About the Stages of Sleep Explained
What Are The Stages Of Sleep?
Light sleep, deep sleep, and REM sleep make up the full sleep cycle.
How Long Is A Normal Sleep Cycle?
Most sleep cycles last 90–110 minutes.
What Is The Most Important Stage Of Sleep?
Deep sleep repairs the body; REM sleep repairs the mind. Both are essential.
How Much REM Sleep Should Adults Get?
Adults need 90–120 minutes per night.
Why Do I Wake Up During The Night?
Stress, sleep disorders, caffeine, screen use, or inconsistent bedtimes can disrupt sleep stages.
Can Supplements Improve Sleep Quality?
Yes — magnesium, melatonin, and herbal teas help regulate sleep cycles.
Does Dreaming Mean I’m Getting Good Sleep?
Dreaming typically means you are entering REM sleep, which is a positive sign — unless nightmares are frequent.
🌙 Conclusion: Mastering Your Sleep Stages for Better Rest
Understanding the stages of sleep explained helps you identify why you might feel tired, stressed, or unfocused — even after a full night in bed. Once you know what your body needs at each stage, you can build habits that support deeper, more restorative sleep.
When you take control of your sleep architecture, you take control of your mood, focus, energy, and overall health.
Tonight is a great night to begin.
⚠️ Sleep Health Disclaimer
This article is for informational purposes only and does not provide medical advice. Always consult a healthcare professional before beginning new supplements, treatments, or sleep therapies, especially if you have chronic insomnia or underlying health conditions.

- Sleep Anxiety: How To Calm Your Mind Before Bed And Finally Rest
- How Many Hours of Sleep Do Adults Really Need?
- Sleep Paralysis Explained